Ethereum, Ethereum Classic, Callisto Network, A Common History
Article published on CoinMarketCal on May 29, 2021.

Ethereum, a Hack and a Hard Fork
During the TheDAO hack, the hackers managed to steal a part of the funds. Under pressure from the community, the Ethereum developers agreed to implement not only updates to prevent such hacks but also to restore the blockchain to the condition it was before the Hack.
When the Ethereum network hard fork took place on 20 July 2016, some node owners did not support the chain rollback because of the blockchain's "immutability" violation. Instead, they continued to support the original blockchain, resulting in two independent networks and two blockchains being maintained; Ethereum Classic was born.
The notion of an immutable blockchain enables some members of the Ethereum Classic community to claim that Ethereum Classic is the original Ethereum. Subsequently, the Ethereum Classic developers changed the monetary policy, reducing the emission from infinity to 210.7 million ETC coins. They also reduced the "difficulty bomb" and introduced several innovations, including those developed for Ethereum.
Ethereum Classic Protocol Improvements
Ethereum Classic is based on a democratic and somewhat complex system for proposal submission and voting. As a result, the process of discussing and voting on proposals can take several months, as well as their approval for deployment in the network.
Ethereum Classic's structure presents both strengths and weaknesses. On the one hand, there is no way for a single person to control the network and decide independently. Still, on the other hand, the time-consuming and laborious decision-making mechanism has led to repeated 51% attacks on the network.
All proposals are subject to the ECIP process, which is actively discussed within the community, as described below:
Draft: An ECIP that is still being worked on and modified, but is ready for pre-examination.
Last Call: An ECIP whose initial version is finalized and ready to be reviewed by a larger audience.
Accepted: An ECIP that has been in the Last Call state for at least 2 weeks and for which all technical changes that were requested have been addressed by the author.
Final: An ECIP that has been accepted, implemented, and cannot be amended without submitting a new proposal (e.g. it has been launched in a hard fork)
Ethereum Classic and the emergence of Callisto Network
As a decentralized project, Ethereum Classic relies on several development teams. One of these was the Ethereum Commonwealth founded by the iconic Dexaran.
Dexaran quickly realized that the ETC protocol improvement process was slow and decided to launch a separate blockchain to address this.
He wrote about this in Ethereum Commonwealth development update (11 Jan, 2018):
“ It may take years to propose any changes to ETC protocol and achieve a consensus on whether we need to implement it or not. As a result, it was decided to launch a separate network to implement the protocol. If the reference implementation succeeds, then we can implement the protocol changes on ETC as well.”
The Callisto network was therefore established with the idea of improving the Ethereum Classic protocol.
Callisto Network, the Self-sustaining and Self-funded Blockchain
The Callisto launch was accompanied by an Airdrop for ETC holders. The snapshot of the Ethereum Classic blockchain was taken at block 5500000 (5 March 2018), and the ETC coins owner received CLO in a 1:1 ratio.
Although a key objective of Callisto Network was the improvement of the ETC protocol, the original white paper also introduced the concept of an audit department for smart contracts, which has become a reference in the field.
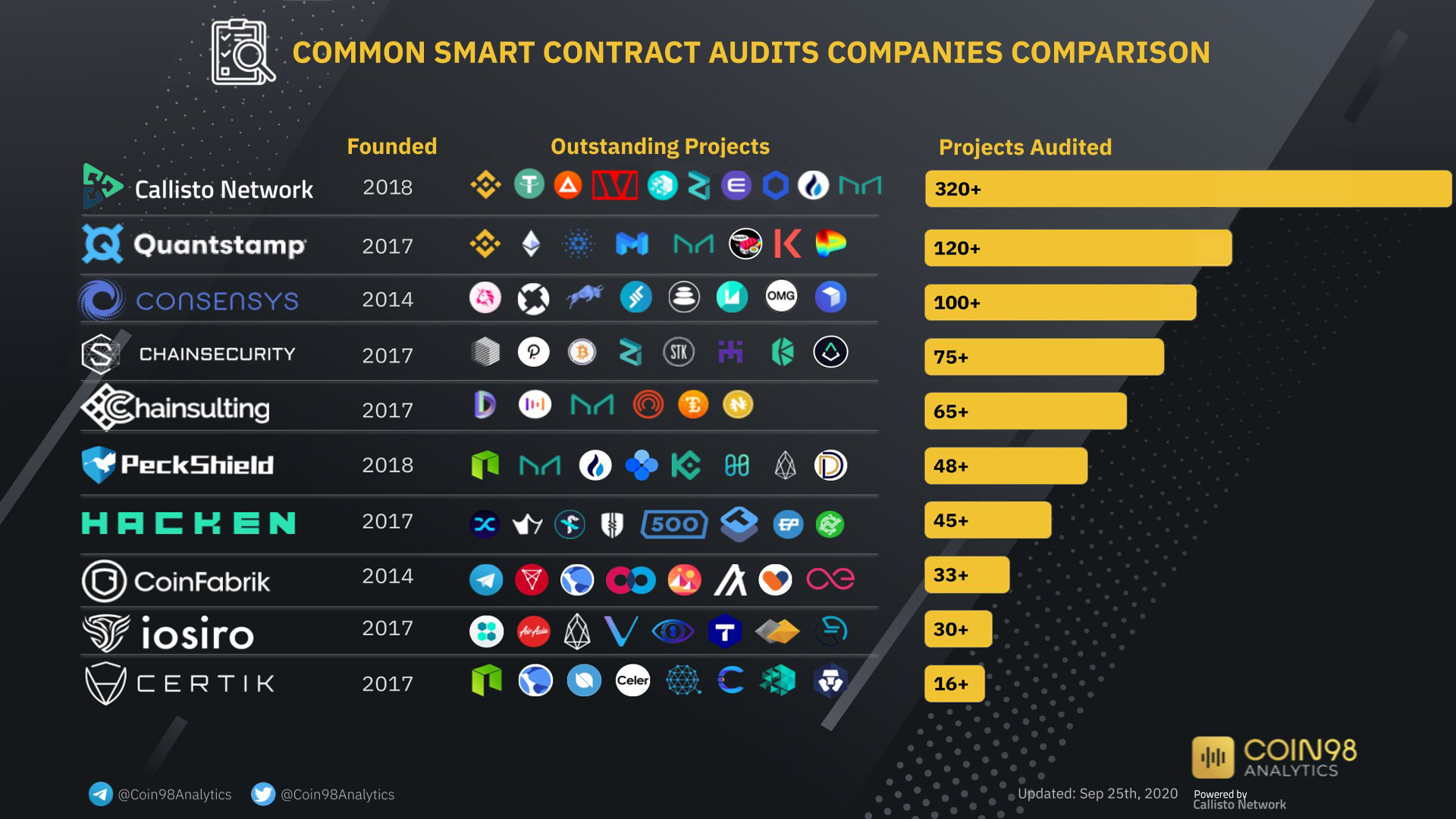
Another matter for Dexaran was reducing the influence of miners on new coin emission, which is why he introduced the concept of Cold Staking.
“ Cold staking is a smart-contract based process that allows CLO holders to earn interest in a total CLO emission when they hold CLO coins at their balances for a long enough period of staking time.”
Dexaran Ethereum Commonwealth development update (11 Jan, 2018).
Over time, Callisto has become a project in its own right. It has become one of the major players in terms of security, proposing improvements to the ETC protocol and EOS, and even in the summer of 2020, an amendment to the Nakamoto consensus.
As for the relationship with the Ethereum Classic, Dexaran and Yohan, co-founders of Callisto Network, stated during an AMA session on March 2, 2020:
Dexaran: “I've been a security engineer and smart-contract developer for the last few years. Security was always my main focus even before coming to the crypto industry. My public activity started here in crypto with TheDAO hard fork and my involvement in Ethereum Classic development.
Honestly, we started Callisto Network to develop and provide a reference implementation for ETC protocol improvements but these were rejected by the ETC community recently so CLO is now a self-sustaining project with its own goals only”.
Yohan Graterol: “I’m a backend developer and I’ve worked as Head of Engineering in some companies. I’ve started working in crypto through ETC with Dexaran and after we launched Callisto Network.
Right now I’m involved with the Callisto community and all legal aspects — listing, marketing, and main development of the Callisto client”.
Read this article on CoinMarketCal.
Original article written by Hashrate-and-Shares.
About Hashrate and Shares:
Hashrate & shares is a blog specialized in articles inspired by the possibilities of blockchain technology.
Twitter: https://twitter.com/hashrateNshares
Telegram: https://t.me/hashrateNshares
Website: https://hashrate-and-shares.ru
Last updated